Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms Strengths
tablets (Zoloft, generic)
- 25mg
- 50mg
- 100mg
capsules (generic)
- 150mg
- 200mg
oral solution (Zoloft, generic)
- 20mg/mL
Major depressive disorder
Indicated for major depressive disorder (MDD)
Tablets
- Initial dose: 50 mg PO qDay
- May increase by 25 mg at weekly intervals; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Capsules
- Do not use to initiate treatment; only available as 150-mg or 200-mg doses
- Use another sertraline HCl product for initial dosage, titration, and dosages below 150 mg qDay
- Refer to prescribing information of other sertraline HCl products for the recommended dosage for those products
- May initiate capsules in patients receiving 100 mg or 125 mg of another sertraline HCl product for at least 1 week
- Recommended dosage: 150 mg or 200 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Indicated for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Tablets
- Initial dose: 50 mg PO qDay
- May increase by 25 mg at weekly intervals; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Capsules
- Do not use to initiate treatment; only available as 150-mg or 200-mg doses
- Use another sertraline HCl product for initial dosage, titration, and dosages below 150 mg qDay
- Refer to prescribing information of other sertraline HCl products for the recommended dosage for those products
- May initiate capsules in patients receiving 100 mg or 125 mg of another sertraline HCl product for at least 1 week
- Recommended dosage: 150 mg or 200 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Panic Disorder
Tablets only
Indicated for panic disorder (PD)
Initial: 25 mg PO qDay
May increase by 25 mg at weekly intervals; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Tablets only
Indicated posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Initial: 25 mg PO qDay
May increase by 25 mg at weekly intervals; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Social Anxiety Disorder
Tablets only
Indicated for social anxiety disorder (SAD)
Initial: 25 mg PO qDay
May increase by 25 mg at weekly intervals; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
Tablets only
Indicated for premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
Continuous dosing
- Initial: 50 mg per day continuously (every day throughout the menstrual cycle)
- May increase by 50 mg per menstrual cycle to up to 150 mg per day if necessary
Intermittent dosing
- Initial: 50 mg per day intermittently (only during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, ie, starting daily dosage 14 days before the anticipated onset of menstruation and continuing through the onset of menses)
- Repeat intermittent dosing with each new cycle
- May increase to a maximum 100 mg per day during the next menstrual cycle
- Subsequent cycles: 50 mg/day during the first 3 days of dosing followed by 100 mg/day during the remaining days in the dosing cycle
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- All severities (eGFR 15-89 mL/min/1.73 m2): No dosage adjustment necessary
- Sertraline exposure does not appear to be affected by renal impairment
Hepatic impairment
Capsules: Dosage adjustments are not possible with available dosage strengths
Tablets
- Mild (Child Pugh scores 5 or 6): Reduce starting and therapeutic range by half the recommended daily dosage; dosage adjustments are not possible with capsules
- Moderate-to-severe (Child Pugh scores 7-15): Not recommended
Dosing Considerations
Before initiating treatment
- Before initiating treatment, screen for personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania
Switching to or from a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)
- When switching to or from a MAOI antidepressant, at least 14 days must elapse between discontinuing MAOI antidepressant and initiating sertraline
- Additionally, at least 14 days must elapse after stopping sertraline capsules before starting an MAOI antidepressant
Discontinuation of sertraline HCl capsules
- Abrupt discontinuation may result in adverse effects including nausea, sweating, dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (eg, paresthesia, tremor, anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, hypomania, tinnitus, and seizures
- Gradually taper dose over at least several weeks to limit possibilities of withdrawal symptoms and detection of re-emerging symptoms
- Consider the half-life of antidepressant when tapering; those with a shorter half-life may require longer and more conservative dose reductions
-
Capsules only
- Given that dosage strengths lower than 150 mg are not available, gradual dosage reduction will require the use of another sertraline HCl product
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablets (Zoloft, generic)
- 25mg
- 50 mg
- 100mg
capsules (generic)
- 150mg
- 200mg
oral solution (Zoloft, generic)
- 20mg/mL
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Indicated for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in adults and children aged ≥6 years
<6 years: Safety and efficacy not established
Tablets
- 6-12 years: 25 mg PO qDay initially
- 12-17 years: 50 mg PO qDay initially
- May increase by 50 mg qDay at weekly intervals, not to exceed 200 mg qDay; give qHS if somnolence experienced
Capsules
- Do not use to initiate treatment; only available as 150-mg or 200-mg doses
- Use another sertraline HCl product for initial dosage, titration, and dosages below 150 mg qDay
- Refer to prescribing information of other sertraline HCl products for the recommended dosage for those products
- May initiate capsules in patients receiving 100 mg or 125 mg of another sertraline HCl product for at least 1 week
- Recommended dosage: 150 mg or 200 mg PO qDay; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- All severities (eGFR 15-89 mL/min/1.73 m2): No dosage adjustment necessary
- Sertraline exposure does not appear to be affected by renal impairment
Hepatic impairment
Capsules: Dosage adjustments are not possible with available dosage strengths
Tablets
- Mild (Child Pugh scores 5 or 6): Reduce starting and therapeutic range by half the recommended daily dosage; dosage adjustments are not possible with capsules
- Moderate-to-severe (Child Pugh scores 7-15): Not recommended
Dosing Considerations
Before initiating treatment
- Before initiating treatment, screen for personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania
Switching to or from a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)
- When switching to or from a MAOI antidepressant, at least 14 days must elapse between discontinuing MAOI antidepressant and initiating sertraline
- Additionally, at least 14 days must elapse after stopping sertraline capsules before starting an MAOI antidepressant
Discontinuation of sertraline HCl capsules
- Abrupt discontinuation may result in adverse effects including nausea, sweating, dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (eg, paresthesia, tremor, anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, hypomania, tinnitus, and seizures
- Gradually taper dose over at least several weeks to limit possibilities of withdrawal symptoms and detection of re-emerging symptoms
- Consider the half-life of antidepressant when tapering; those with a shorter half-life may require longer and more conservative dose reductions
-
Capsules only
- Given that dosage strengths lower than 150 mg are not available, gradual dosage reduction will require the use of another sertraline HCl product
The elderly are prone to SSRI/SNRI-induced hyponatremia; monitor closely
Major Depressive Disorder
25 mg PO qDay initially; may increase by 25 mg every 2-3 days; not to exceed 200 mg qDay
Alzheimer dementia related depression: Start at 12.5 mg/day and titrate every 1-2 weeks to response; not to exceed 150-200 mg
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment: Dose adjustment not necessary
Mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh 5-6): Decrease recommended starting dose and therapeutic dose by 50%
Moderate-to-severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh 7-15): Not recommended; sertraline is extensively metabolized, and the effects in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment have not been studied
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (13)
- dronedarone
sertraline and dronedarone both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- eliglustat
sertraline increases levels of eliglustat by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Contraindicated. If coadministered with strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors, reduce eliglustat dose from 84 mg BID to 84 mg once daily in extensive and intermediate metabolizers; eliglustat is contraindiated if strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors are given concomitantly with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors.
- flibanserin
sertraline will increase the level or effect of flibanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of flibanserin with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated. Severe hypotension or syncope can occur.
- isocarboxazid
isocarboxazid and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
- lomitapide
sertraline increases levels of lomitapide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Increases lomitapide levels several folds.
- lonafarnib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of lonafarnib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Lonafarnib is a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate. Coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors is contraindicated.
- mavacamten
sertraline will increase the level or effect of mavacamten by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong or moderate CYP2C19 inhibitors may increase mavacamten systemic exposure, resulting in heart failure due to systolic dysfunction.
- phenelzine
phenelzine and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
- pimozide
sertraline increases levels of pimozide by decreasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Risk of prolonged QTc interval.
- procarbazine
procarbazine and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated. Combination is contraindicated within 2 weeks of MAOI use.
- selegiline
selegiline and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated. At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of selegiline and initiation of treatment with a serotonergic drug.
- thioridazine
sertraline increases levels of thioridazine by decreasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Risk of long QT syndrome.
sertraline and thioridazine both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated. - tranylcypromine
tranylcypromine and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Contraindicated.
Serious - Use Alternative (161)
- adagrasib
adagrasib, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Each drug prolongs the QTc interval, which may increased the risk of Torsade de pointes, other serious arryhthmias, and sudden death. If coadministration unavoidable, more frequent monitoring is recommended for such patients.
- alfentanil
alfentanil, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amiodarone
sertraline and amiodarone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amisulpride
amisulpride and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. ECG monitoring is recommended if coadministered.
- amitriptyline
sertraline and amitriptyline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amoxapine
sertraline and amoxapine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- anagrelide
sertraline and anagrelide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of apalutamide, a strong CYP2C19 inducer, with drugs that are CYP2C19 substrates can result in lower exposure to these medications. Avoid or substitute another drug for these medications when possible. Evaluate for loss of therapeutic effect if medication must be coadministered.
- arsenic trioxide
sertraline and arsenic trioxide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- artemether
artemether and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- artemether/lumefantrine
sertraline and artemether/lumefantrine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- asenapine
sertraline and asenapine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- asenapine transdermal
asenapine transdermal and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- avapritinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of avapritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of avapritinib with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors. If unable to avoid, reduce avapritinib starting dose. See drug monograph Dosage Modifications.
- axitinib
sertraline increases levels of axitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, monitor closely and reduce dose if necessary .
- bosutinib
sertraline increases levels of bosutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine
sertraline and buprenorphine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine buccal
buprenorphine buccal and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
buprenorphine subdermal implant and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine transdermal
buprenorphine transdermal and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
buprenorphine, long-acting injection and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buspirone
sertraline and buspirone both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ceritinib
ceritinib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- chlorpromazine
sertraline and chlorpromazine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- citalopram
citalopram and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Combination may increase risk of serotonin syndrome or neuroleptic malignant syndrome-like reactions.
citalopram and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - clarithromycin
clarithromycin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- clomipramine
sertraline and clomipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sertraline and clomipramine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - cobimetinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of cobimetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concurrent short term (14 days or less) use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable for patients who are taking cobimetinib 60 mg, reduce the cobimetinib dose to 20 mg. After discontinuation of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor, resume cobimetinib 60 mg. Use an alternative to a moderate CYP3A inhibitor in patients who are taking a reduced dose of cobimetinib (40 or 20 mg daily).
- crizotinib
crizotinib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cyclobenzaprine
sertraline and cyclobenzaprine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dacomitinib
dacomitinib will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid use with CYP2D6 substrates where minimal increases in concentration of the CYP2D6 substrate may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- desflurane
desflurane and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- desipramine
sertraline and desipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
desipramine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - desvenlafaxine
sertraline and desvenlafaxine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dextromethorphan
sertraline and dextromethorphan both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- disopyramide
sertraline and disopyramide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dofetilide
dofetilide increases toxicity of sertraline by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dolasetron
dolasetron, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dosulepin
sertraline and dosulepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- doxepin
sertraline and doxepin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxepin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - droperidol
sertraline and droperidol both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- duloxetine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
duloxetine and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - elacestrant
sertraline will increase the level or effect of elacestrant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eliglustat
sertraline increases levels of eliglustat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors are not recommended with eliglustat poor or intermediate metabolizers; reduce eliglustat dose from 84 mg BID to 84 mg once daily in extensive metabolizers .
- encorafenib
encorafenib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- entrectinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of entrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors with entrectinib, a CYP3A4 substrate. If coadministration unavoidable, reduce dose to 200 mg/day for patients aged 12 y or older with BSA >1.50m2. Resume previous entrectinib dose after discontinuing moderate CYP3A inhibitor for 3-5 elimination half-lives.
entrectinib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - eribulin
eribulin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin base
sertraline and erythromycin base both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
sertraline and erythromycin ethylsuccinate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin stearate
sertraline and erythromycin stearate both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- escitalopram
escitalopram and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
escitalopram increases toxicity of sertraline by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fedratinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of fedratinib by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of fedratinib (a CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 substrate) with dual CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 inhibitor. Effect of coadministration of a dual CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 inhibitor with fedratinib has not been studied.
- fentanyl
sertraline will increase the level or effect of fentanyl by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals and consider fentanyl dose adjustments until stable drug effects are achieved.
fentanyl, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fentanyl intranasal
sertraline will increase the level or effect of fentanyl intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals and consider fentanyl dose adjustments until stable drug effects are achieved.
fentanyl intranasal, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fentanyl transdermal
sertraline will increase the level or effect of fentanyl transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals and consider fentanyl dose adjustments until stable drug effects are achieved.
fentanyl transdermal, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fentanyl transmucosal
sertraline will increase the level or effect of fentanyl transmucosal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is necessary, monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals and consider fentanyl dose adjustments until stable drug effects are achieved.
fentanyl transmucosal, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fexinidazole
fexinidazole and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of fexinidazole with drugs known to block potassium channels or prolong QT interval.
- flecainide
sertraline and flecainide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fluoxetine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of fluoxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
fluoxetine and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - fluvoxamine
fluvoxamine and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sertraline and fluvoxamine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - foscarnet
sertraline and foscarnet both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- gilteritinib
gilteritinib will decrease the level or effect of sertraline by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of gilteritinib with drugs that inhibit 5HT2B or sigma nonspecific receptors. Avoid use of these drugs with gilteritinib unless coadministration is necessary.
- givinostat
sertraline and givinostat both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration, obtain ECGs when initiating, during concomitant use, and as clinically indicated. Withhold if QTc interval >500 ms or a change from baseline >60 ms.
- givosiran
givosiran will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP2D6 substrates with givosiran. If unavoidable, decrease the CYP2D6 substrate dosage in accordance with approved product labeling.
- glasdegib
sertraline and glasdegib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- granisetron
granisetron, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- hydromorphone
hydromorphone, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- hydroxychloroquine sulfate
hydroxychloroquine sulfate and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ibrutinib
sertraline increases levels of ibrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, reduce ibrutinib dose to 280 mg qDay (B-cell malignancies) or 420 mg qDay (graft versus host disease). After CYP3A inhibitor discontinuation, resume previous dose of ibrutinib.
- ibutilide
sertraline and ibutilide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- iloperidone
sertraline and iloperidone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- imipramine
sertraline and imipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sertraline and imipramine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - infigratinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of infigratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- inotuzumab
sertraline and inotuzumab both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- irinotecan
sertraline will increase the level or effect of irinotecan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- irinotecan liposomal
sertraline will increase the level or effect of irinotecan liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- isoflurane
isoflurane and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ivabradine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of ivabradine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of ivabradine with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- ivosidenib
ivosidenib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of QTc prolonging drugs with ivosidenib or replace with alternate therapies. If coadministration of a QTc prolonging drug is unavoidable, monitor for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation.
- lefamulin
lefamulin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lemborexant
sertraline will increase the level or effect of lemborexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of lemborexant with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors.
- lenvatinib
sertraline and lenvatinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- levomilnacipran
levomilnacipran and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- linezolid
linezolid and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Linezolid may increase serotonin as a result of MAO-A inhibition. If linezolid must be administered, discontinue serotonergic drug immediately and monitor for CNS toxicity. Serotonergic therapy may be resumed 24 hours after last linezolid dose or after 2 weeks of monitoring, whichever comes first.
- lofepramine
sertraline and lofepramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lofexidine
sertraline and lofexidine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lopinavir
sertraline and lopinavir both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lorcaserin
sertraline and lorcaserin both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lurbinectedin
sertraline will increase the level or effect of lurbinectedin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- macimorelin
macimorelin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Macimorelin causes an increase of ~11 msec in the corrected QT interval. Avoid coadministration with drugs that prolong QT interval, which could increase risk for developing torsade de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia. Allow sufficient washout time of drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval before administering macimorelin.
- maprotiline
sertraline and maprotiline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mefloquine
mefloquine increases toxicity of sertraline by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Mefloquine may enhance the QTc prolonging effect of high risk QTc prolonging agents.
- meperidine
sertraline and meperidine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
meperidine, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - methadone
sertraline and methadone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- methylene blue
methylene blue and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Methylene blue may increase serotonin as a result of MAO-A inhibition. If methylene blue must be administered, discontinue serotonergic drug immediately and monitor for CNS toxicity. Serotonergic therapy may be resumed 24 hours after last methylene blue dose or after 2 weeks of monitoring, whichever comes first.
- metoclopramide
metoclopramide and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Additive effects; increased risk for serotonin syndrome, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, dystonia, or other extrapyramidal reactions
- metoclopramide intranasal
sertraline, metoclopramide intranasal. Either increases effects of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Avoid use of metoclopramide intranasal or interacting drug, depending on importance of drug to patient.
- midazolam intranasal
sertraline will increase the level or effect of midazolam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors with midazolam intranasal causes higher midazolam systemic exposure, which may prolong sedation.
- midostaurin
sertraline and midostaurin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- milnacipran
milnacipran and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mobocertinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of mobocertinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor unavoidable, reduce mobocertinib dose by ~50% (eg, 160 to 80 mg); closely monitor QTc interval.
mobocertinib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, reduce mobocertinib dose and monitor QTc interval more frequently. - morphine
morphine, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- moxifloxacin
sertraline and moxifloxacin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- naloxegol
sertraline will increase the level or effect of naloxegol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministation of naloxegol with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce naloxegol dose to 12.5 mg qDay
- nefazodone
nefazodone and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- neratinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of neratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of neratinib with strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- netupitant/palonosetron
netupitant/palonosetron, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nilotinib
sertraline and nilotinib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nirogacestat
sertraline will increase the level or effect of nirogacestat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nortriptyline
sertraline and nortriptyline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sertraline and nortriptyline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - olaparib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of olaparib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with moderate CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce olaparib dose to 200 mg (capsule) or 150 mg (tablet) PO BID. Do not substitute tablets with capsules.
- olopatadine intranasal
sertraline and olopatadine intranasal both increase sedation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration increases risk of CNS depression, which can lead to additive impairment of psychomotor performance and cause daytime impairment.
- omaveloxolone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of omaveloxolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unavoidable, reduce omaveloxolone dose to 100 mg/day. Closely monitor for adverse effects. If adverse effects emerge, further reduce to 50 mg/day.
- ondansetron
ondansetron and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid with congenital long QT syndrome; ECG monitoring recommended with concomitant medications that prolong QT interval, electrolyte abnormalities, CHF, or bradyarrhythmias.
ondansetron, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - oxaliplatin
oxaliplatin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ozanimod
ozanimod increases toxicity of sertraline by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Because the active metabolite of ozanimod inhibits MAO-B in vitro, there is a potential for serious adverse reactions, including hypertensive crisis. Therefore, coadministration of ozanimod with drugs that can increase norepinephrine or serotonin is not recommended. Monitor for hypertension with concomitant use.
- pacritinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of pacritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- paliperidone
sertraline and paliperidone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- palonosetron
palonosetron, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- panobinostat
sertraline and panobinostat both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- paroxetine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of paroxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
paroxetine and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - pazopanib
sertraline and pazopanib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pemigatinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of pemigatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce pemigatinib dose (refer to drug monograph dosage modifications). After discontinuing the CYP3A4 inhibitor for 3 elimination half-lives, may resume previous pemigatinib dose.
- pentamidine
sertraline and pentamidine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pexidartinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of pexidartinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce pexidartinib dose (refer to drug monograph dosage modifications). After discontinuing the CYP3A4 inhibitor for 3 elimination half-lives, may resume previous pexidartinib dose.
- phentermine
sertraline, phentermine. Either increases toxicity of the other by Mechanism: unknown. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of serotonin syndrome.
- pimavanserin
sertraline and pimavanserin both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pimozide
sertraline and pimozide both increase QTc interval. Contraindicated.
- pitolisant
sertraline and pitolisant both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ponesimod
sertraline and ponesimod both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- procainamide
sertraline and procainamide both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- protriptyline
sertraline and protriptyline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sertraline and protriptyline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - quetiapine
sertraline and quetiapine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rasagiline
rasagiline and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Severe CNS toxicity associated with hyperpyrexia has been reported with the combined treatment of an antidepressant and rasagiline. Avoid combination within 14 days of MAOI use.
- remifentanil
remifentanil, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- repotrectinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of repotrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Discontinue strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors and wait 3-5 elimination half-lives before initiating repotrectinib.
- ribociclib
ribociclib increases toxicity of sertraline by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- saquinavir
sertraline and saquinavir both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selegiline transdermal
selegiline transdermal and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selinexor
selinexor, sertraline. unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Patients treated with selinexor may experience neurological toxicities. Avoid taking selinexor with other medications that may cause dizziness or confusion.
- selumetinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of selumetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce selumetinib dosage (refer to selumetinib monograph for further information). After discontinuation of the strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor for 3 elimination half-lives, resume selumetinib dose that was taken before initiating the inhibitor.
- sevoflurane
sevoflurane and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- siponimod
sertraline will increase the level or effect of siponimod by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of siponimod with a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor PLUS a moderate or strong CYP2C9 inhibitor is not recommended.
sertraline and siponimod both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
siponimod and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - St John's Wort
sertraline and St John's Wort both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sufentanil
sufentanil, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tazemetostat
sertraline will increase the level or effect of tazemetostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of tazemetostat with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors. If coadministration is unavoidable, reduce tazemetostat current dose (see drug monograph Dosage Modifications).
- tedizolid
tedizolid, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. both increase serotonin levels; increased risk of serotonin syndrome.
- tetrabenazine
sertraline and tetrabenazine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- thioridazine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of thioridazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- toremifene
sertraline and toremifene both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trazodone
sertraline and trazodone both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sertraline and trazodone both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - trimipramine
sertraline and trimipramine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sertraline and trimipramine both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled
sertraline increases toxicity of umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol inhaled by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution when vilanterol coadministered with drugs that prolong QTc interval; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
- vandetanib
sertraline and vandetanib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vemurafenib
sertraline and vemurafenib both increase QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- venetoclax
sertraline will increase the level or effect of venetoclax by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If a moderate CYP3A inhibitor must be used, reduce the venetoclax dose by at least 50%. Monitor more closely for signs of venetoclax toxicities.
- venlafaxine
sertraline and venlafaxine both increase serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sertraline and venlafaxine both decrease QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled
sertraline increases toxicity of vilanterol/fluticasone furoate inhaled by QTc interval. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Exercise extreme caution when vilanterol coadministered with drugs that prolong QTc interval; adrenergic agonist effects on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
- vilazodone
sertraline, vilazodone. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant therapy should be discontinued immediately if signs or symptoms of serotonin syndrome emerge and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated. .
- vortioxetine
sertraline, vortioxetine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- zuranolone
sertraline, zuranolone. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of zuranolone with other CNS depressants may increase impairment of psychomotor performance or CNS depressant effects. If unavoidable, consider dose reduction. .
Monitor Closely (266)
- 5-HTP
sertraline and 5-HTP both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- abiraterone
abiraterone increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid coadministration of abiraterone with substrates of CYP2D6. If alternative therapy cannot be used, exercise caution and consider a dose reduction of the CYP2D6 substrate.
- acalabrutinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of acalabrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Decrease acalabrutinib dose to 100 mg once daily if coadministered with a moderate CYP3A inhibitor.
- aceclofenac
sertraline, aceclofenac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- acemetacin
sertraline, acemetacin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- albuterol
albuterol and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alfuzosin
sertraline and alfuzosin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
alfuzosin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - almotriptan
almotriptan and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- amifampridine
sertraline increases toxicity of amifampridine by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Comment: Amifampridine can cause seizures. Coadministration with drugs that lower seizure threshold may increase this risk.
- amitriptyline
sertraline and amitriptyline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amoxapine
sertraline and amoxapine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- apixaban
sertraline and apixaban both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. SSRIs may inhibit platelet aggregation, thus increase bleeding risk when coadministered with anticoagulants.
- apomorphine
apomorphine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- arformoterol
arformoterol and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aripiprazole
sertraline will increase the level or effect of aripiprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
aripiprazole and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - aspirin
sertraline, aspirin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- aspirin rectal
sertraline, aspirin rectal. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate
sertraline, aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- atazanavir
atazanavir increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity. .
- atogepant
sertraline will increase the level or effect of atogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atomoxetine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of atomoxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
atomoxetine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - avanafil
sertraline will increase the level or effect of avanafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP3A4 inhibitors may reduce avanafil clearance increasing systemic exposure to avanafil; increased levels may result in increased associated adverse events; the maximum recommended dose of STENDRA is 50 mg, not to exceed once every 24 hours for patients taking concomitant moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors
- bedaquiline
sertraline and bedaquiline both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. ECG should be monitored closely
- benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen
sertraline will increase the level or effect of benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hydromorphone (<3% of the circulating parent hydrocodone [benzhydrocodone is prodrug of hydrocodone]) is mainly formed by CYP2D6 mediated O-demethylation of hydrocodone. Hydromorphone may contribute to the total analgesic effect of hydrocodone.
benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment. - betrixaban
sertraline, betrixaban. Either increases levels of the other by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. SSRIs may inhibit platelet aggregation, thus increase bleeding risk when coadministered with anticoagulants.
- brexpiprazole
sertraline will increase the level or effect of brexpiprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administer a quarter of brexpiprazole dose if coadministered with a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor PLUS a strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor.
sertraline will increase the level or effect of brexpiprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administer a quarter of brexpiprazole dose if coadministered with a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor PLUS a strong/moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor. - buprenorphine subdermal implant
sertraline will increase the level or effect of buprenorphine subdermal implant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor patients already on buprenorphine subdermal implant who require newly-initiated treatment with CYP3A4 inhibitors for signs and symptoms of overmedication. If the dose of the concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be reduced or discontinued, implant removal may be necessary and the patient should then be treated with a buprenorphine dosage form that permits dose adjustments. If a CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued in a patient who has been stabilized on buprenorphine, monitor the patient for withdrawal.
sertraline, buprenorphine subdermal implant. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use could result in life-threatening serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation, and during dose adjustment of the serotonergic drug. Discontinue buprenorphine if serotonin syndrome is suspected. - buprenorphine, long-acting injection
sertraline will increase the level or effect of buprenorphine, long-acting injection by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Patients who transfer to buprenorphine long-acting injection from transmucosal buprenorphine coadministered with CYP3A4 inhibitors should be monitored to ensure buprenorphine plasma levels are adequate. Within 2 weeks, if signs and symptoms of buprenorphine toxicity or overdose occur and the concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be reduced or discontinued, transition the patient back to a buprenorphine formulation that permits dose adjustments.
sertraline, buprenorphine, long-acting injection. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use could result in life-threatening serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation, and during dose adjustment of the serotonergic drug. Discontinue buprenorphine if serotonin syndrome is suspected. - bupropion
sertraline increases levels of bupropion by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sertraline may inhibit hydroxylation of bupropion to its major active metabolite hydroxybupropion.
bupropion will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - cabozantinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of cabozantinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cannabidiol
sertraline will increase the level or effect of cannabidiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the cannabidiol dose when coadministered with a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor.
cannabidiol will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of sensitive CYP2C19 substrates, as clinically appropriate, when coadministered with cannabidiol. - capivasertib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of capivasertib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce capivasertib dose if coadministered with moderate CYP3A inhibitors.
- carvedilol
sertraline will increase the level or effect of carvedilol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- celecoxib
sertraline, celecoxib. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- cenobamate
cenobamate will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a dose reduction of CYP2C19 substrates, as clinically appropriate, when used concomitantly with cenobamate.
cenobamate, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. - choline magnesium trisalicylate
sertraline, choline magnesium trisalicylate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- cilostazol
sertraline increases toxicity of cilostazol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider decreasing cilostazol dose; moderate CYP2C19 inhibitors may increase serum levels of 3,4-dehydrocilostazol (active metabolite).
- ciprofloxacin
sertraline and ciprofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clobazam
clobazam will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lower doses of drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 may be required when used concomitantly.
- clomipramine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of clomipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- clonidine
clonidine, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration enhances CNS depressant effects.
- clopidogrel
sertraline increases effects of clopidogrel by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. SSRIs affect platelet activation; coadministration of SSRIs with clopidogrel may increase the risk of bleeding.
- clozapine
sertraline increases levels of clozapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Plasma levels of clozapine may be increased, resulting in increased pharmacologic and toxic effects. Adjust clozapine dose as needed when initiating or discontinuing certain SSRIs. .
clozapine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - cobicistat
cobicistat will increase the level or effect of sertraline by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Carefully titrate dose of the antidepressant to the desired effect, including using the lowest feasible initial or maintenance dose, and monitor its response during coadministration with SSRIs and cobicistat.
- cocaine topical
sertraline and cocaine topical both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- codeine
sertraline decreases effects of codeine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Prevents conversion of codeine to its active metabolite morphine.
- cyproheptadine
cyproheptadine decreases effects of sertraline by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Cyproheptadine may diminish the serotonergic effect of SSRIs.
- daridorexant
sertraline will increase the level or effect of daridorexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Daridorexant dose should not exceed 25 mg per night when coadministered with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
sertraline and daridorexant both increase sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration increases risk of CNS depression, which can lead to additive impairment of psychomotor performance and cause daytime impairment. - darunavir
darunavir decreases levels of sertraline by Mechanism: unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Carefully titrate SSRI dose based on clinical assessment of antidepressant response.
darunavir will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with SSRIs, TCAs, or trazodone may require dose titration of antidepressant to desired effect (eg, using the lowest feasible initial or maintenance dose). Monitor for antidepressant response. - dasatinib
dasatinib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- defibrotide
defibrotide increases effects of sertraline by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Defibrotide may enhance effects of platelet inhibitors.
- deflazacort
sertraline will increase the level or effect of deflazacort by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Decrease deflazacort dose to one-third of the recommended dose if coadministered with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- degarelix
degarelix and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- desipramine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of desipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- deutetrabenazine
deutetrabenazine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. At the maximum recommended dose, deutetrabenazine does not prolong QT interval to a clinically relevant extent. Certain circumstances may increase risk of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with drugs that prolong the QTc interval (eg, bradycardia, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, coadministration with other drugs that prolong QTc interval, presence of congenital QT prolongation).
- dexfenfluramine
sertraline and dexfenfluramine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dextroamphetamine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of dextroamphetamine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
sertraline and dextroamphetamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - dextroamphetamine transdermal
sertraline, dextroamphetamine transdermal. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Initiate with lower doses and monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue dextroamphetamine transdermal and concomitant serotonergic drug(s).
- diazepam intranasal
sertraline will increase the level or effect of diazepam intranasal by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP2C19 inhibitors may decrease rate of diazepam elimination, thereby increasing adverse reactions to diazepam.
sertraline will increase the level or effect of diazepam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may decrease rate of diazepam elimination, thereby increasing adverse reactions to diazepam.
diazepam intranasal, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may potentiate the CNS-depressant effects of each drug. - diclofenac
sertraline, diclofenac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- difelikefalin
difelikefalin and sertraline both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diflunisal
sertraline, diflunisal. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- dihydroergotamine
sertraline and dihydroergotamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dihydroergotamine intranasal
sertraline and dihydroergotamine intranasal both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dolasetron
dolasetron and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- donepezil
donepezil and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- edoxaban
sertraline increases effects of edoxaban by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of bleeding.
- efavirenz
efavirenz will decrease the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
efavirenz and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - eletriptan
eletriptan and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- eliglustat
eliglustat increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations, as indicated, or consider reducing the dosage of the concomitant drug and titrate to clinical effect.
sertraline and eliglustat both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Cobicistat is a CYP2D6 inhibitor; caution with CYP2D6 substrates for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events.
- ergotamine
sertraline and ergotamine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- erythromycin lactobionate
sertraline and erythromycin lactobionate both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eslicarbazepine acetate
eslicarbazepine acetate will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etodolac
sertraline, etodolac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- fedratinib
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP2C19 substrates as necessary.
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP2D6 substrates as necessary. - fenbufen
sertraline, fenbufen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- fenfluramine
sertraline and fenfluramine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
fenfluramine, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with drugs that increase serotoninergic effects may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. - fenoprofen
sertraline, fenoprofen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- fexinidazole
fexinidazole will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- finerenone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of finerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor serum potassium during initiation and dosage adjustment of either finererone or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors. Adjust finererone dosage as needed.
- fingolimod
fingolimod and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fish oil triglycerides
fish oil triglycerides will increase the level or effect of sertraline by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Prolonged bleeding reported in patients taking antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants and oral omega-3 fatty acids. Periodically monitor bleeding time in patients receiving fish oil triglycerides and concomitant antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants.
- fluconazole
sertraline and fluconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluoxetine
sertraline and fluoxetine both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- flurbiprofen
sertraline, flurbiprofen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- fondaparinux
sertraline increases effects of fondaparinux by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of bleeding.
- fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity. .
- fosphenytoin
sertraline increases levels of fosphenytoin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fostemsavir
sertraline and fostemsavir both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. QTc prolongation reported with higher than recommended doses of fostemsavir.
- frovatriptan
frovatriptan and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- gabapentin
gabapentin, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- gabapentin enacarbil
gabapentin enacarbil, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- ganaxolone
sertraline and ganaxolone both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gemifloxacin
gemifloxacin and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- gepirone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of gepirone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce gepirone dose by 50% when used concomitantly with a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor.
gepirone and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
gepirone and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for symptoms of serotonin syndrome when gepirone is used gepirone with other drugs that may affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems. If serotonin syndrome occurs, consider discontinue gepirone and/or concomitant serotonergic drug. - gilteritinib
gilteritinib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- goserelin
sertraline and goserelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- granisetron
granisetron and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- grapefruit
grapefruit will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- green tea
green tea, sertraline. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Combination may increase risk of bleeding.
- guanfacine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of guanfacine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors significantly increase guanfacine plasma concentrations. FDA-approved labeling for extended-release (ER) guanfacine recommends that, if coadministered, the guanfacine dosage should be decreased to half of the recommended dose. Specific recommendations for immediate-release (IR) guanfacine are not available.
- haloperidol
sertraline will increase the level or effect of haloperidol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
haloperidol and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - histrelin
sertraline and histrelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydrocodone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of hydrocodone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hydromorphone (<3% of the circulating parent hydrocodone) is mainly formed by CYP2D6 mediated O-demethylation of hydrocodone. Hydromorphone may contribute to the total analgesic effect of hydrocodone.
hydrocodone, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment. - hydromorphone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of hydromorphone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydroxyzine
hydroxyzine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ibrutinib
ibrutinib will increase the level or effect of sertraline by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Ibrutinib may increase the risk of hemorrhage in patients receiving antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapies and monitor for signs of bleeding.
- ibuprofen
sertraline, ibuprofen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- ibuprofen IV
sertraline, ibuprofen IV. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- icosapent
icosapent, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Icosapent may prolong bleeding time. Periodically monitor if coadministered with other drugs that affect bleeding.
- ifosfamide
sertraline decreases effects of ifosfamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration .
- iloperidone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of iloperidone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- imipramine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- indapamide
sertraline and indapamide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- indinavir
indinavir increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity. .
- indomethacin
sertraline, indomethacin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- ioflupane I 123
sertraline decreases effects of ioflupane I 123 by receptor binding competition. Use Caution/Monitor. Drugs that bind to dopamine transporter receptor with high affinity may interfere with the image following ioflupane I 123 administration.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
sertraline will increase the level or effect of isavuconazonium sulfate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isoniazid
sertraline and isoniazid both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- itraconazole
itraconazole and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ivacaftor
sertraline will increase the level or effect of ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce ivacaftor dose if coadministered with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors. See specific ivacaftor-containing product for precise dosage modification.
- ivosidenib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of ivosidenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase ivosidenib plasma concentrations, thus increasing the risk of QTc prolongation. Monitor for increased risk of QTc interval prolongation.
- ketoprofen
sertraline, ketoprofen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- ketorolac
sertraline, ketorolac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- ketorolac intranasal
sertraline, ketorolac intranasal. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- L-tryptophan
sertraline and L-tryptophan both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lamotrigine
lamotrigine increases toxicity of sertraline by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. CNS depressants may increase the toxic effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; psychomotor impairment may be enhanced.
- lapatinib
sertraline and lapatinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of lasmiditan and other CNS depressant drugs, including alcohol have not been evaluated in clinical studies. Lasmiditan may cause sedation, as well as other cognitive and/or neuropsychiatric adverse reactions.
sertraline increases effects of lasmiditan by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may increase risk of serotonin syndrome. - lefamulin
sertraline will increase the level or effect of lefamulin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for adverse effects if lefamulin is coadministered with moderate CYP3A inhibitors.
- lemborexant
lemborexant, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Dosage adjustment may be necessary if lemborexant is coadministered with other CNS depressants because of potentially additive effects.
- letermovir
letermovir increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- leuprolide
sertraline and leuprolide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levamlodipine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of levamlodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with moderate and strong CYP3A inhibitors results in increased systemic exposure to amlodipine and may require dose reduction. Monitor for symptoms of hypotension and edema when amlodipine is coadministered with CYP3A inhibitors to determine the need for dose adjustment.
- levofloxacin
sertraline and levofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lisdexamfetamine
sertraline, lisdexamfetamine. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Initiate with lower doses and monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue along with concomitant serotonergic drug(s).
- lithium
sertraline and lithium both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
lithium and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - lofepramine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of lofepramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- loperamide
sertraline and loperamide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lopinavir
lopinavir increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity.
- lorcaserin
lorcaserin will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lornoxicam
sertraline, lornoxicam. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- lsd
sertraline and lsd both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
lumacaftor/ivacaftor, sertraline. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. In vitro studies suggest that lumacaftor may induce and ivacaftor may inhibit CYP2C19 substrates. .
lumacaftor/ivacaftor will decrease the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. A higher dose of sertraline may be required to obtain desired therapeutic effect. Sertraline is a substrate of CYP3A4, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP2B6. Lumacaftor/ivacaftor is a strong inducer of CYP3A and lumacaftor has the potential to induce CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP2B6. - lumateperone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of lumateperone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce lumateperone dose to 21 mg/day if coadministered with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- lurasidone
lurasidone, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Potential for increased CNS depressant effects when used concurrently; monitor for increased adverse effects and toxicity.
- maprotiline
sertraline and maprotiline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- maraviroc
maraviroc increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity. .
- mavacamten
sertraline will increase the level or effect of mavacamten by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Inititiation of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may require decreased mavacamten dose.
- meclofenamate
sertraline, meclofenamate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- mefenamic acid
sertraline, mefenamic acid. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- mefloquine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of mefloquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- meloxicam
sertraline, meloxicam. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- metformin
sertraline increases effects of metformin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methamphetamine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of methamphetamine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methylphenidate transdermal
methylphenidate transdermal will increase the level or effect of sertraline by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider decreasing the dose of these drugs when given coadministered with methylphenidate. Monitor for drug toxiticities when initiating or discontinuing methylphenidate.
- metoprolol
sertraline will increase the level or effect of metoprolol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- midazolam intranasal
midazolam intranasal, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol, or other CNS depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect.
- mifepristone
mifepristone, sertraline. QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Use alternatives if available.
- mipomersen
mipomersen, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Both drugs have potential to increase hepatic enzymes; monitor LFTs.
- mirabegron
mirabegron will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mirtazapine
sertraline and mirtazapine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
mirtazapine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - morphine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of morphine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
sertraline and morphine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - nabumetone
sertraline, nabumetone. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- naldemedine
sertraline increases levels of naldemedine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor naldemedine for potential adverse effects if coadministered with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- naproxen
sertraline, naproxen. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- naratriptan
naratriptan and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nebivolol
sertraline will increase the level or effect of nebivolol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nelfinavir
nelfinavir increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity. .
- nevirapine
nevirapine will decrease the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- norgestrel
sertraline will increase the level or effect of norgestrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase systemic concentration of norgestrel, which may increase risk for adverse effects
- nortriptyline
sertraline will increase the level or effect of nortriptyline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- octreotide
sertraline and octreotide both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ofloxacin
sertraline and ofloxacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- olanzapine
olanzapine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- olanzapine/samidorphan
sertraline, olanzapine/samidorphan. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of diazepam, alcohol, or other CNS acting drugs may potentiate orthostatic hypotension observed with olanzapine. Additive sedation may also occur.
- oliceridine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of oliceridine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If concomitant use is necessary, may require less frequent oliceridine dosing. Closely monitor for respiratory depression and sedation and titrate subsequent doses accordingly. If inhibitor is discontinued, consider increase oliceridine dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal.
sertraline will increase the level or effect of oliceridine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If concomitant use is necessary, may require less frequent oliceridine dosing. Closely monitor for respiratory depression and sedation and titrate subsequent doses accordingly. If inhibitor is discontinued, consider increase oliceridine dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal.
sertraline, oliceridine. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - osilodrostat
osilodrostat and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- osimertinib
osimertinib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. Conduct periodic monitoring with ECGs and electrolytes in patients taking drugs known to prolong the QTc interval.
- oxaprozin
sertraline, oxaprozin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- oxycodone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of oxycodone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
oxycodone increases effects of sertraline by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Opioids may enhance the serotonergic effects of SSRIs and increase risk for serotonergic syndrome. - oxymorphone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of oxymorphone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ozanimod
ozanimod and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The potential additive effects on heart rate, treatment with ozanimod should generally not be initiated in patients who are concurrently treated with QT prolonging drugs with known arrhythmogenic properties.
- palbociclib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of palbociclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- palovarotene
sertraline will increase the level or effect of palovarotene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid coadministration of palovarotene, a CYP3A substrate, with moderate CYP3A inhibitors. If unavoidable, reduce palovarotene dose by 50%.
- parecoxib
sertraline, parecoxib. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- paroxetine
sertraline and paroxetine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pasireotide
sertraline and pasireotide both increase QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- peginterferon alfa 2b
peginterferon alfa 2b, sertraline. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: When patients are administered peginterferon alpha-2b with CYP2D6 substrates, the therapeutic effect of these drugs may be altered. Peginterferon alpha-2b may increase or decrease levels of CYP2D6 substrate.
- pentazocine
sertraline and pentazocine both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- perphenazine
sertraline and perphenazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenytoin
sertraline increases levels of phenytoin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- piroxicam
sertraline, piroxicam. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- posaconazole
sertraline and posaconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pregabalin
pregabalin, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation.
- primaquine
primaquine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
sertraline and primaquine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - prochlorperazine
sertraline and prochlorperazine both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- promethazine
sertraline and promethazine both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- propranolol
sertraline will increase the level or effect of propranolol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sertraline is a moderate to weak inhibitor of the hepatic (CYP2D6) which may be involved in the metabolism of propranolol. Monitor patients receiving propranolol and sertraline cotherapy for an increased incidence of chest pain. This effect may be more pronounced in patients with preexisting coronary artery disease.
- quinine
sertraline and quinine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quizartinib
quizartinib, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor patients more frequently with ECG if coadministered with QT prolonging drugs.
- ranolazine
sertraline and ranolazine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- remimazolam
remimazolam, sertraline. Either increases toxicity of the other by sedation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and/or death. Continuously monitor vital signs during sedation and recovery period if coadministered. Carefully titrate remimazolam dose if administered with opioid analgesics and/or sedative/hypnotics.
- rilpivirine
sertraline and rilpivirine both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rimegepant
sertraline will increase the level or effect of rimegepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid repeating rimegepant dose within 48 hr if coadministered with a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- risperidone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of risperidone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
sertraline and risperidone both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - ritonavir
ritonavir increases levels of sertraline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of serotonin syndrome.
- rivaroxaban
sertraline increases effects of rivaroxaban by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Combination may increase risk of bleeding.
- rizatriptan
rizatriptan and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- rolapitant
rolapitant will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Rolapitant may increase plasma concentrations of CYP2D6 substrates for at least 28 days following rolapitant administration.
- romidepsin
sertraline and romidepsin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rucaparib
rucaparib will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Adjust dosage of CYP2C19 substrates, if clinically indicated.
- ruxolitinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ruxolitinib topical
sertraline will increase the level or effect of ruxolitinib topical by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- safinamide
sertraline, safinamide. Either increases toxicity of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor patients for symptoms of serotonin syndrome if SSRIs are coadministered with safinamide.
- salicylates (non-asa)
sertraline, salicylates (non-asa). Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- salsalate
sertraline, salsalate. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- SAMe
sertraline and SAMe both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- selpercatinib
selpercatinib increases toxicity of sertraline by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride
sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride increases effects of sertraline by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Closely monitor for evidence of seizures when using bowel preps together with drugs that lower the seizure threshold.
- sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol
sertraline, sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Caution when bowel preps are used with drugs that cause SIADH or NSAIDs; increased risk for water retention or electrolyte imbalance.
- sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate
sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate increases effects of sertraline by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Closely monitor for evidence of seizures when using bowel preps together with drugs that lower the seizure threshold.
- solifenacin
sertraline and solifenacin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sonidegib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of sonidegib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid coadministration of sonidegib with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors. If a moderate CYP3A inhibitor must be used, administer the moderate CYP3A inhibitor for <14 days and monitor closely for adverse reactions, particularly musculoskeletal adverse reactions.
- sorafenib
sorafenib and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sotalol
sertraline and sotalol both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sparsentan
sertraline will increase the level or effect of sparsentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. No dosage adjustment needed. Monitor blood pressure, serum potassium, edema, and kidney function regularly if sparsentan is coadministered with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
sparsentan will decrease the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sparsentan (a CYP2C19 inducer) decreases exposure of CYP2C19 substrates and reduces efficacy related to these substrates. - stiripentol
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of CYP2C19 substrates, if adverse reactions are experienced when administered concomitantly with stiripentol.
stiripentol, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by sedation. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use stiripentol with other CNS depressants, including alcohol, may increase the risk of sedation and somnolence. - sufentanil SL
sufentanil SL, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by serotonin levels. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system may result in serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dose adjustment.
sertraline will increase the level or effect of sufentanil SL by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of sufentanil SL with any CYP3A4 inhibitor may increase sufentanil plasma concentration, and, thereby increase or prolonged adverse effects, including potentially fatal respiratory depression. - sulfasalazine
sertraline, sulfasalazine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- sulindac
sertraline, sulindac. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- sumatriptan
sumatriptan and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sumatriptan intranasal
sumatriptan intranasal and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- sunitinib
sertraline and sunitinib both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- suvorexant
sertraline will increase the level or effect of suvorexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Decrease suvorexant starting dose to 5 mg HS if coadministered with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors
- tacrolimus
sertraline and tacrolimus both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tadalafil
sertraline will increase the level or effect of tadalafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP3A4 inhibitors may reduce tadalafil clearance increasing systemic exposure to tadalafil; increased levels may result in increased associated adverse events.
- tamoxifen
sertraline decreases effects of tamoxifen by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Inhibition of CYP2D6 metabolism to tamoxifen's active metabolite, endoxifen.
- tamsulosin
sertraline increases levels of tamsulosin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tapentadol
sertraline and tapentadol both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tecovirimat
tecovirimat will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Tecovirimat is a weak inhibitor of CYP2C8 and CYP2C19. Monitor for adverse effects if coadministered with sensitive substrates of these enzymes.
- telavancin
sertraline and telavancin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- terbinafine
terbinafine will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Assess need to reduce dose of CYP2D6-metabolized drug.
- tezacaftor
sertraline will increase the level or effect of tezacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Adjust tezacaftor dosage regimen if coadministered with a moderate CYP3A inhibitor.
- timolol
sertraline will increase the level or effect of timolol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tinidazole
sertraline will increase the level or effect of tinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tofacitinib
sertraline increases levels of tofacitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. No specific dose adjustment recommended when tofacitinib coadministered with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors; decrease tofacitinib dose if coadministered with both moderate CYP3A4 and potent CYP2C19 inhibitors.
- tolfenamic acid
sertraline, tolfenamic acid. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- tolmetin
sertraline, tolmetin. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
- trabectedin
sertraline will increase the level or effect of trabectedin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tramadol
sertraline decreases effects of tramadol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Decreased conversion of tramadol to active metabolite.
sertraline and tramadol both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
sertraline decreases effects of tramadol by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Decreased conversion of tramadol to active metabolite. - triclabendazole
triclabendazole will increase the level or effect of sertraline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. If plasma concentrations of the CYP2C19 substrates are elevated during triclabendazole, recheck plasma concentration of the CYP2C19 substrates after discontinuation of triclabendazole.
sertraline and triclabendazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - trifluoperazine
sertraline and trifluoperazine both decrease QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- triptorelin
sertraline and triptorelin both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- valbenazine
valbenazine and sertraline both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- valerian
valerian and sertraline both increase sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vardenafil
sertraline and vardenafil both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
sertraline will increase the level or effect of vardenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Vardenafil dose may need to be reduced if coadministered with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors - voclosporin
sertraline will increase the level or effect of voclosporin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce voclosporin daily dosage to 15.8 mg PO in AM and 7.9 mg PO in PM.
voclosporin, sertraline. Either increases effects of the other by QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor. - vorapaxar
sertraline, vorapaxar. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive antiplatelet effect may occur; SSRIs and SNRIs may cause platelet serotonin depletion .
- voriconazole
sertraline and voriconazole both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vorinostat
sertraline and vorinostat both increase QTc interval. Use Caution/Monitor.
- warfarin
sertraline, warfarin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. SSRIs and SNRIs may increase anticoagulation effect of warfarin. .
- zanubrutinib
sertraline will increase the level or effect of zanubrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Reduce zanubrutinib (a CYP3A4 substrate) to 80 mg PO BID to when coadministered with a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor. Interrupt dose as recommended for adverse reactions. After discontinuing the CYP3A4 inhibitor, resume previous dose of zanubrutinib.
sertraline, zanubrutinib. Either increases effects of the other by anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Zanubrutinib-induced cytopenias increases risk of hemorrhage. Coadministration of zanubritinib with antiplatelets or anticoagulants may further increase this risk. - ziprasidone
sertraline and ziprasidone both decrease QTc interval. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- zolmitriptan
zolmitriptan and sertraline both increase serotonin levels. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Minor (45)
- almotriptan
sertraline, almotriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- azithromycin
azithromycin increases toxicity of sertraline by QTc interval. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- bumetanide
bumetanide, sertraline. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive hyponatremia.
- carbamazepine
sertraline increases levels of carbamazepine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- celandine
celandine decreases effects of sertraline by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Based on animal studies.
- chloroquine
chloroquine increases toxicity of sertraline by QTc interval. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chlorpromazine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of chlorpromazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- codeine
sertraline decreases effects of codeine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Decreased conversion of codeine to active metabolite morphine.
- dexfenfluramine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of dexfenfluramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dexmethylphenidate
dexmethylphenidate increases effects of sertraline by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dextromethorphan
sertraline will increase the level or effect of dextromethorphan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- donepezil
sertraline will increase the level or effect of donepezil by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- doxepin
sertraline will increase the level or effect of doxepin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- eletriptan
sertraline, eletriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- encainide
sertraline will increase the level or effect of encainide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- esmolol
sertraline increases levels of esmolol by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- estradiol vaginal
sertraline will increase the level or effect of estradiol vaginal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ethacrynic acid
ethacrynic acid, sertraline. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive hyponatremia.
- fesoterodine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of fesoterodine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- flecainide
sertraline will increase the level or effect of flecainide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Monitor the EKG in patients receiving concurrent flecainide and sertraline. Doses of flecainide may need to be reduced.
- fluphenazine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of fluphenazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- frovatriptan
sertraline, frovatriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- furosemide
furosemide, sertraline. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive hyponatremia.
- galantamine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of galantamine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- lithium
sertraline, lithium. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of neurotoxicity.
- loratadine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of loratadine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- mexiletine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of mexiletine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- naratriptan
sertraline, naratriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- panax ginseng
panax ginseng increases effects of sertraline by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- perhexiline
sertraline will increase the level or effect of perhexiline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- perphenazine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of perphenazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pleurisy root
pleurisy root decreases effects of sertraline by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction.
- prochlorperazine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of prochlorperazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- promazine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of promazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- promethazine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of promethazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- propafenone
sertraline will increase the level or effect of propafenone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Monitor the EKG in patients receiving concurrent propafenone and sertraline. Doses of propafenone may need to be reduced.
- rizatriptan
sertraline, rizatriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate
serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate increases effects of sertraline by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sumatriptan
sertraline, sumatriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- sumatriptan intranasal
sertraline, sumatriptan intranasal. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
- tolterodine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of tolterodine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- torsemide
torsemide, sertraline. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive hyponatremia.
- trifluoperazine
sertraline will increase the level or effect of trifluoperazine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tropisetron
sertraline will increase the level or effect of tropisetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- zolmitriptan
sertraline, zolmitriptan. Mechanism: unknown. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of weakness, dyspnea, chest pain.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Nausea (26%)
Diarrhea/loose stools (20%)
Insomnia (20%)
Dry mouth (14%)
Fatigue (12%)
Dizziness (12%)
Somnolence (11%)
1-10%
Tremor (9%)
Dyspepsia (8%)
Ejaculation failure (8%)
Agitation (8%)
Decreased appetite (7%)
Hyperhidrosis (7%)
Libido decreased (6-7%)
Constipation (6%)
Palpitations (4%)
Visual impairment (4%)
Vomiting (4%)
Erectile dysfunction (4%)
Ejaculation disorder (3%)
Male sexual dysfunction (2%)
<2%
- Cardiac disorders – Tachycardia
- Ear and labyrinth disorders – Tinnitus
- Endocrine disorders – Hypothyroidism
- Eye disorders - Mydriasis, blurred vision
- Gastrointestinal disorders - Hematochezia, melena, rectal hemorrhage
- General disorders and administration site conditions - Edema, gait disturbance, irritability, pyrexia
- Hepatobiliary disorders - Elevated liver enzymes
- Immune system disorders – Anaphylaxis
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders - Diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, hypoglycemia, increased appetite
- Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders - Arthralgia, muscle spasms, tightness, or twitching
- Nervous system disorders - Ataxia, coma, convulsion, decreased alertness, hypoesthesia, lethargy, psychomotor hyperactivity, syncope
- Psychiatric disorders - Aggression, bruxism, confusional state, euphoric mood, hallucination
- Renal and urinary disorders – Hematuria
- Reproductive system and breast disorders – Galactorrhea, priapism, vaginal hemorrhage
- Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders - Bronchospasm, epistaxis, yawning
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders – Alopecia, cold sweat; dermatitis; dermatitis bullous; pruritus; purpura; erythematous, follicular, or maculopapular rash; urticaria Vascular disorders - hemorrhage, hypertension, vasodilation
Postmarketing Reports
- Bleeding or clotting disorders - Increased coagulation times (altered platelet function)
- Cardiac disorders - AV block, bradycardia, atrial arrhythmias, QTc-interval prolongation, ventricular tachycardia (including torsade de pointes)
- Endocrine disorders - Gynecomastia, hyperprolactinemia, menstrual irregularities, SIADH
- Eye disorders - Blindness, optic neuritis, cataract
- Hepatobiliary disorders - Severe liver events (including hepatitis, jaundice, liver failure with some fatal outcomes), pancreatitis
- Hemic and lymphatic disorders - Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia and pancytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, lupus-like syndrome, serum sickness
- Immune system disorders – Angioedema
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders - Hyponatremia, hyperglycemia
- Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders - Rhabdomyolysis, trismus
- Nervous system disorders - Serotonin syndrome, extrapyramidal symptoms (including akathisia and dystonia), oculogyric crisis, anosmia, hyposmia
- Psychiatric disorders - Psychosis, enuresis, paranoia
- Renal and urinary disorders - Acute renal failure
- Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders - Pulmonary hypertension, eosinophilic pneumonia
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders - Photosensitivity skin reaction and other severe cutaneous reactions, which potentially can be fatal, such as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
- Vascular disorders - Cerebrovascular spasm (including reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome and Call-Fleming syndrome), vasculitis
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Suicidal thoughts and behaviors
- Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in pediatric and young adult patients in short-term studies
- Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity
Do not use disulfiram concomitantly with oral solution due to alcohol in preparation
Concomitant pimozide: Risk of long QT syndrome
Coadministration with serotonergic drugs
- Do not use MAOIs concomitantly or within 14 days before initiating sertraline or within 14 days after discontinuing sertraline
- Reactions to concomitant administration with MAO inhibitors include tremor, myoclonus, diaphoresis, nausea, vomiting, flushing, dizziness, hyperthermia with features resembling neuroleptic malignant syndrome, seizures, rigidity, autonomic instability with possible rapid fluctuations of vital signs, and mental status changes that include extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma
- Starting sertraline in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or IV methylene blue is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome
- If linezolid or IV methylene blue must be administered, discontinue SSRI immediately and monitor for CNS toxicity; may resume 24 hr after last linezolid or methylene blue dose, or after 2 weeks of monitoring (5 weeks for fluoxetine), whichever comes first
Cautions
Clinical worsening and suicide ideation may occur despite medication
Use caution in patients with seizure disorders
May worsen mania symptoms or precipitate mania in patients with bipolar disorder
Increases risk of hyponatremia and impairment of cognitive/motor functions in the elderly
Increases risk of bleeding in patients taking anticoagulants/antiplatelets concomitantly
Risk of mydriasis; may trigger angle closure attack in patients with angle closure glaucoma with anatomically narrow angles without a patent iridectomy
Avoid abrupt withdrawal
Bone fractures reported with antidepressant therapy; consider the possibility if patient presents with bone pain, bruising, or point of tenderness
Coadministration with other drugs that enhance the effects of serotonergic neurotransmission (eg, tryptophan, fenfluramine, fentanyl, 5-HT agonists, meperidine, methadone, St. John’s Wort) should be undertaken with caution and avoided whenever possible due to the potential for pharmacodynamic interaction (see Contraindications); serotonin syndrome can also occur when these drugs are used alone
May cause false-positive urine immunoassay screening tests for benzodiazepines
SSRIs and SNRIs are associated with development of SIADH; hyponatremia reported
Sexual dysfunction
- Use may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction in both male and female patients; inform patients that they should discuss any changes in sexual function and potential management strategies with their healthcare provider
- Use of SSRIs, may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction; in male patients, SSRI use may result in ejaculatory delay or failure, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction
- In female patients, SSRI/SNRI use may result in decreased libido and delayed or absent orgasm
- Important for prescribers to inquire about sexual function prior to initiation of therapy and to inquire specifically about changes in sexual function during treatment, because sexual function may not be spontaneously reported
- When evaluating changes in sexual function, obtaining a detailed history (including timing of symptom onset) is important because sexual symptoms may have other causes, including underlying psychiatric disorder
- Discuss potential management strategies to support patients in making informed decisions about treatment
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Overall, available published epidemiologic studies of pregnant women exposed to sertraline in the first trimester suggest no difference in major birth defect risk compared to the background rate for major birth defects in comparator populations
Some studies have reported increases for specific major birth defects; however, these study results are inconclusive
There are clinical considerations regarding neonates exposed to SSRIs during the third trimester of pregnancy
In neonates exposed to SNRIs/SSRIs late in third trimester: Risk of complications such as feeding difficulties, irritability, and respiratory problems
Exposure to SSRIs, particularly in month before delivery, associated with <2-fold increase in risk of postpartum hemorrhage; bleeding events related to drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake have ranged from ecchymosis, hematoma, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages
Use in the month before delivery may be associated with an increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage
Pregnancy exposure registry
- Monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antidepressants during pregnancy
- Encourage patients to enroll by calling the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants at 1-866-961-2388 or visiting online at https://womensmentalhealth.org/research/pregnancyregistry/antidepressants
Lactation
Available data from published literature demonstrate low levels of sertraline and its metabolites in human milk
There are no data on the effects of sertraline on milk production
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; little or no affinity for alpha-adrenergic histamine or cholinergic receptor
Absorption
Bioavailability: Absorption increased by food
Peak plasma time: 4.5-8.4 hr
Distribution
Protein bound: 98%
Metabolism
Metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes
Metabolites: Minimal potency
Elimination
Half-life: 26 hr
Dialyzable: No
Excretion: Urine (12-14% unchanged); feces (40-45%)
Pharmacogenomics
Several SSRIs (eg, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline) are metabolized by CYP2D6
CYP2D6 is involved in the metabolism of approximately 20% of drugs in clinical use and displays large individual-to-individual variability in activity due to genetic polymorphisms
More than 80 CYP2D6 variant alleles have been identified; however, 4 of the most prevalent alleles, CYP2D6*3, *4, *5, and *6, account for 93-97% of CYP2D6 poor metabolizers
CYP2D6*4, the most common variant (~25% frequency in whites), causes a splicing defect; CYP2D6*3 (2.7% frequency) causes a frameshift mutation; and CYP3D6*5 (2.6%) is an entire deletion of the CYP2D6 gene; individuals homozygous for these alleles have no CYP2D6 activity
The impact of CYP2D6 activity is further complicated in some SSRIs (eg, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline) because in addition to being substrates for CYP2D6, they are also known to moderately inhibit CYP2D6 activity
Genetic testing laboratories
- Genotyping tests for CYP2D6 variants are commercially available through the following companies
- Applied Biosystems (http://www.appliedbiosystems.com/)
- GenPath Diagnostics (http://www.genpathdiagnostics.com/)
Administration
Oral Administration
Tablets or capsules: May take with or without food
Capsules
- Swallow capsule whole; do not open, crush, or chew
Oral solution preparation
- Must be diluted before administration
- Measure dose with calibrated dropper supplied; dropper has 25 mg and 50 mg graduation marks only
- Mix dose with 4 oz of water, ginger ale, lemon/lime soda, lemonade, or orange juice only
- A slight haze may appear, which is normal
- Swallow dose immediately after mixing
Storage
Store at 20-25ºC (68-77ºF); excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| sertraline oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 100 mg tablet | 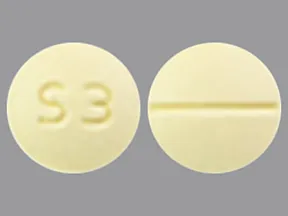 | |
| sertraline oral - | 50 mg tablet | 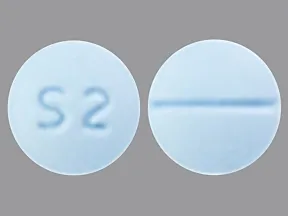 | |
| sertraline oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 20 mg/mL liquid | 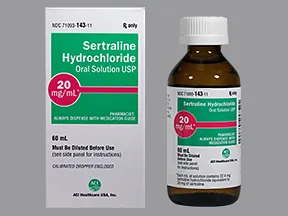 | |
| sertraline oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 100 mg tablet | 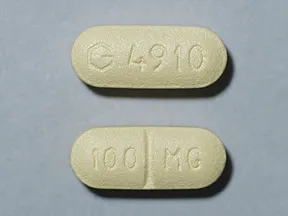 | |
| sertraline oral - | 100 mg tablet | 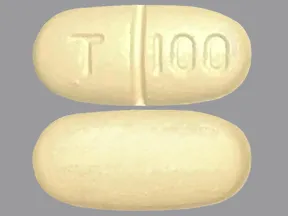 | |
| sertraline oral - | 50 mg tablet | 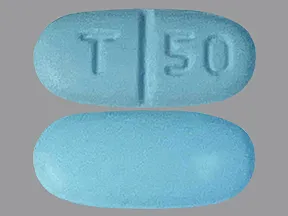 | |
| sertraline oral - | 50 mg tablet | 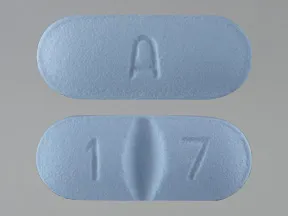 | |
| sertraline oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 50 mg tablet | 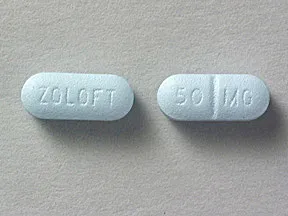 | |
| sertraline oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 100 mg tablet | 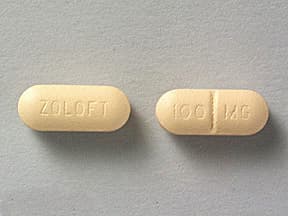 | |
| sertraline oral - | 25 mg tablet | 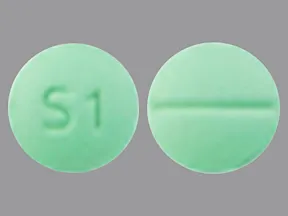 | |
| sertraline oral - | 20 mg/mL liquid |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 150 mg capsule |  | |
| sertraline oral - | 20 mg/mL liquid |  | |
| Zoloft oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Zoloft oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Zoloft oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| Zoloft oral - | 20 mg/mL liquid | 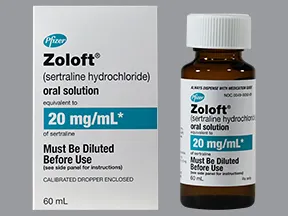 |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
sertraline oral
SERTRALINE - ORAL
(SER-truh-leen)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Zoloft
WARNING: Antidepressant medications are used to treat a variety of conditions, including depression and other mental/mood disorders. These medications can help prevent suicidal thoughts/attempts and provide other important benefits. However, a small number of people (especially people younger than 25) who take antidepressants for any condition may experience worsening depression, other mental/mood symptoms, or suicidal thoughts/attempts. It is very important to talk with the doctor about the risks and benefits of antidepressant medication (especially for people younger than 25), even if treatment is not for a mental/mood condition.Tell the doctor right away if you notice worsening depression/other psychiatric conditions, unusual behavior changes (including possible suicidal thoughts/attempts), or other mental/mood changes (including new/worsening anxiety, panic attacks, trouble sleeping, irritability, hostile/angry feelings, impulsive actions, severe restlessness, very rapid speech). Be especially watchful for these symptoms when a new antidepressant is started or when the dose is changed.
USES: This medication is used to treat certain mental/mood disorders (such as depression, panic attacks, obsessive compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, social anxiety disorder). It is also used to treat a severe form of premenstrual syndrome (premenstrual dysphoric disorder). Sertraline belongs to a class of drugs known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). It works by helping to restore the balance of a certain natural substance (serotonin) in the brain.
HOW TO USE: Read the Medication Guide and, if available, the Patient Information Leaflet provided by your pharmacist before you start using sertraline and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.Take this medication by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually once daily either in the morning or evening. The tablet or liquid form of this medication may be taken with or without food.The 25 milligrams, 50 milligrams, and 100 milligrams capsule is usually taken with food. The 150 milligrams and 200 milligrams capsule may be taken with or without food. Swallow the capsules whole. Do not crush or chew the capsules. If you have any questions about how to take the capsule form of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.The liquid form of this medication must be mixed with another liquid before use. Just before taking, carefully measure the dose using the medicine dropper provided. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose. Mix the dose with a half cup (4 ounces/120 milliliters) of water, ginger ale, lemon-lime soda, lemonade, or orange juice. Do not use other liquids to mix this drug. The mixture may appear cloudy, which is normal and harmless. Drink all of the mixture right away. Do not prepare a supply in advance.If you are taking this medication for premenstrual problems, your doctor may direct you to take this drug every day of the month or for only the 2 weeks before your period until the start of your period.The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. To reduce your risk of side effects, your doctor may direct you to start this medication at a low dose and gradually increase your dose. Follow your doctor's instructions carefully. Take this medication regularly to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, take it at the same time each day.Keep taking this medication even if you feel well. Do not stop taking this medication without consulting your doctor. Some conditions may become worse when this drug is suddenly stopped. Also, you may experience symptoms such as mood swings, headache, tiredness, sleep changes, and brief feelings similar to electric shock. To prevent these symptoms while you are stopping treatment with this drug, your doctor may reduce your dose gradually. Report any new or worsening symptoms right away.Tell your doctor if your condition lasts or gets worse.
SIDE EFFECTS: See also Warning section.Nausea, dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, loss of appetite, increased sweating, diarrhea, upset stomach, or trouble sleeping may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: easy bleeding/bruising, decreased interest in sex, changes in sexual ability, muscle cramps/weakness, shaking (tremor), unusual weight loss.Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: fast/irregular heartbeat, fainting, black stools, vomit that looks like coffee grounds, eye pain/swelling/redness, widened pupils, vision changes (such as seeing rainbows around lights at night, blurred vision).This medication may increase serotonin and rarely cause a very serious condition called serotonin syndrome/toxicity. The risk increases if you are also taking other drugs that increase serotonin, so tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you take (see Drug Interactions section). Get medical help right away if you develop some of the following symptoms: fast heartbeat, hallucinations, loss of coordination, severe dizziness, severe nausea/vomiting/diarrhea, twitching muscles, unexplained fever, unusual agitation/restlessness.Rarely, males may have a painful or prolonged erection lasting 4 or more hours. If this occurs, stop using this drug and get medical help right away, or permanent problems could occur.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking sertraline, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients (such as latex found in the medicine dropper, tartrazine found in some brands), which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: personal or family history of bipolar/manic-depressive disorder, bleeding problems, liver disease, seizure disorder, thyroid disease, personal or family history of glaucoma (angle-closure type).Sertraline may cause a condition that affects the heart rhythm (QT prolongation). QT prolongation can rarely cause serious (rarely fatal) fast/irregular heartbeat and other symptoms (such as severe dizziness, fainting) that need medical attention right away.The risk of QT prolongation may be increased if you have certain medical conditions or are taking other drugs that may cause QT prolongation. Before using sertraline, tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you take and if you have any of the following conditions: certain heart problems (heart failure, slow heartbeat, QT prolongation in the EKG), family history of certain heart problems (QT prolongation in the EKG, sudden cardiac death).Low levels of potassium or magnesium in the blood may also increase your risk of QT prolongation. This risk may increase if you use certain drugs (such as diuretics/"water pills") or if you have conditions such as severe sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting. Talk to your doctor about using sertraline safely.This drug may make you dizzy or drowsy. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness until you can do it safely. Avoid alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis).The liquid form of this medication contains alcohol. Caution is advised if you have diabetes, alcohol dependence, or liver disease. Some medications (such as metronidazole, disulfiram) can cause a serious reaction when combined with alcohol. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about using this product safely.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially bleeding, loss of coordination, or QT prolongation (see above). Loss of coordination can increase the risk of falling. Older adults may also be more likely to develop a type of salt imbalance (hyponatremia), especially if they are taking "water pills" (diuretics).Children may be more sensitive to the side effects of the drug, especially loss of appetite and weight loss. Monitor weight and height in children who are taking this drug.During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. It may harm an unborn baby. Also, babies born to mothers who have used this drug during the last 3 months of pregnancy may rarely develop withdrawal symptoms such as feeding/breathing difficulties, seizures, muscle stiffness, or constant crying. If you notice any of these symptoms in your newborn, tell the doctor promptly.Since untreated mental/mood problems (such as depression, panic attacks, obsessive compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder) can be a serious condition, do not stop taking this medication unless directed by your doctor. If you are planning pregnancy, become pregnant, or think you may be pregnant, discuss with your doctor right away the benefits and risks of using this medication during pregnancy.This drug passes into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: See also Precautions section.Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug are: pimozide, other drugs that can cause bleeding/bruising (including antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel, NSAIDs such as ibuprofen/naproxen, "blood thinners" such as dabigatran/warfarin).Taking MAO inhibitors with this medication may cause a serious (possibly fatal) drug interaction. Avoid taking MAO inhibitors (isocarboxazid, linezolid, metaxalone, methylene blue, moclobemide, phenelzine, procarbazine, rasagiline, safinamide, selegiline, tranylcypromine) during treatment with this medication. Most MAO inhibitors should also not be taken for two weeks before and after treatment with this medication. Ask your doctor when to start or stop taking this medication.The risk of serotonin syndrome/toxicity increases if you are also taking other drugs that increase serotonin. Examples include street drugs such as MDMA/"ecstasy," St. John's wort, certain antidepressants (including other SSRIs such as fluoxetine/paroxetine, SNRIs such as duloxetine/venlafaxine), tryptophan, among others. The risk of serotonin syndrome/toxicity may be more likely when you start or increase the dose of these drugs.Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking other products that cause drowsiness such as alcohol, marijuana (cannabis), antihistamines (such as cetirizine, diphenhydramine), drugs for sleep or anxiety (such as alprazolam, diazepam, zolpidem), muscle relaxants, and opioid pain or cough relievers (such as codeine, hydrocodone).Check the labels on all your medicines (such as allergy or cough-and-cold products) because they may contain ingredients that cause drowsiness. Ask your pharmacist about using those products safely.Aspirin can increase the risk of bleeding when used with this medication. However, if your doctor has told you to take low-dose aspirin to prevent heart attack or stroke (usually 81-162 milligrams a day), you should keep taking the aspirin unless your doctor tells you not to.This medication may interfere with certain medical/lab tests (including brain scan for Parkinson's disease), possibly causing false test results. Make sure lab personnel and all your doctors know you use this drug.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may include: severe dizziness, fainting.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Keep all regular medical and psychiatric appointments.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised March 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.




